rfid tag magnetic field A static magnetic field caused by a normal magnet should not cause any harm to a RFID-tag. Its all about speed of the movement of the RFID-Tag relative to the magnetic field. The antenna (a coil) of the RFID chip and the magnet form a generator. I use a MIFARE Classic NFC access card. Is there any way to clone my card on an Android device (e.g. on Samsung Galaxy Nexus or Asus Nexus 7)? Note: this question is .Go to développer options , disable miui optimizations. Enable the option to allow apps to write to external memory . You will be able to format the memory card as internal storage. However .
0 · what is rfid labels
1 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
2 · rfid magnetic field
3 · rfid chip
4 · radio frequency identification tags are
5 · magnetic field damage rfid tags
6 · magnetic field damage rfid
7 · example of rfid tags
$39.99
A static magnetic field caused by a normal magnet should not cause any harm to a RFID-tag. Its all about speed of the movement of the RFID-Tag relative to the magnetic field. The antenna (a coil) of the RFID chip and the magnet form a generator.MAGNETIC FLUX IN RFID SYSTEMS. This chapter presents an overview of the physical . This paper presents a novel inkjet-printed near-field ultra-high-frequency (UHF) .A static magnetic field caused by a normal magnet should not cause any harm to a RFID-tag. Its all about speed of the movement of the RFID-Tag relative to the magnetic field. The antenna (a coil) of the RFID chip and the magnet form a generator.
MAGNETIC FLUX IN RFID SYSTEMS. This chapter presents an overview of the physical modeling e®orts of inductive RFID tags in the context of corrosivity sensing. Tutorial in nature, the variety of behaviors arising from magnetic °ux coupling from reader to RF tag are explored. This paper presents a novel inkjet-printed near-field ultra-high-frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag/sensor design with uniform magnetic field characteristics. The proposed tag is designed using the theory of characteristics mode (TCM).
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a mature technology that allows contactless data readout via a wireless communication link. While numerous passive RFID tags are available on the market.
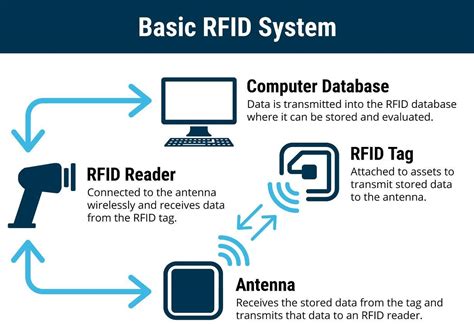
Low frequency (LF, 125-134 KHz) and high frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz) RFID systems are short range systems based on inductive coupling between the reader and the tag antennas through a magnetic field.Introduction. RFID tags extract all of their power to both operate and communicate from the reader’s magnetic field. Coupling between the tag and reader is via the mutual inductance of the two loop antennas, see Figure 1. In this article, we will delve into the impact of magnetic fields on the performance of RFID tags, specifically when exposed to substances like electronic devices and anti-theft systems. This paper proposes an intermittent magnetic field monitoring system based on passive ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. A magnetic field magnitude sensor has been integrated into a micro-controller unit (MCU) based tag, and the standard RFID communication protocol ISO/IEC 18000-6 Type C has been .
Explore how magnetic fields from electronic devices and anti-theft systems affect RFID tags and the performance of RFID library solutions. When an RFID reader emits RF signals, they create an alternating magnetic field. The antenna of the passive tag intercepts this magnetic field, inducing an electrical current through the principle of electromagnetic induction. This induced current serves as the power supply for the tag’s microchip.A static magnetic field caused by a normal magnet should not cause any harm to a RFID-tag. Its all about speed of the movement of the RFID-Tag relative to the magnetic field. The antenna (a coil) of the RFID chip and the magnet form a generator.MAGNETIC FLUX IN RFID SYSTEMS. This chapter presents an overview of the physical modeling e®orts of inductive RFID tags in the context of corrosivity sensing. Tutorial in nature, the variety of behaviors arising from magnetic °ux coupling from reader to RF tag are explored.
This paper presents a novel inkjet-printed near-field ultra-high-frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) tag/sensor design with uniform magnetic field characteristics. The proposed tag is designed using the theory of characteristics mode (TCM).
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a mature technology that allows contactless data readout via a wireless communication link. While numerous passive RFID tags are available on the market.Low frequency (LF, 125-134 KHz) and high frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz) RFID systems are short range systems based on inductive coupling between the reader and the tag antennas through a magnetic field.Introduction. RFID tags extract all of their power to both operate and communicate from the reader’s magnetic field. Coupling between the tag and reader is via the mutual inductance of the two loop antennas, see Figure 1. In this article, we will delve into the impact of magnetic fields on the performance of RFID tags, specifically when exposed to substances like electronic devices and anti-theft systems.
This paper proposes an intermittent magnetic field monitoring system based on passive ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. A magnetic field magnitude sensor has been integrated into a micro-controller unit (MCU) based tag, and the standard RFID communication protocol ISO/IEC 18000-6 Type C has been .Explore how magnetic fields from electronic devices and anti-theft systems affect RFID tags and the performance of RFID library solutions.
stanley rfid tags

what is rfid labels
rfid radio frequency identification tags
• A Comprehensive Technical Overview of Contactless• Contactless.info, archived from the original on 24 April 2014 is designed to provide information for UK retailers that have an interest in Contactless card acceptance] See more
rfid tag magnetic field|what is rfid labels